Employee burnout is a widespread issue that affects both productivity and employee well-being. With workplace stress contributing to 60% of absences and costing U.S. companies up to $190 billion annually, businesses are seeking better ways to address it. AI offers a solution by predicting burnout with 70% accuracy, using data from workplace tools, communication sentiment, and wearables.
Key Takeaways:
- What AI Does: Identifies burnout risks early by analyzing behavioral, emotional, and physiological data.
- How It Works: Tracks patterns like missed breaks, negative language in emails, and sleep disruptions.
- Why It Matters: Early detection helps reduce turnover, absenteeism, and healthcare costs.
- Tools in Action: Platforms like Aidx.ai provide team-level insights and 24/7 support without invading privacy.
AI-driven tools shift burnout management from reactive to preventative, offering a smarter way to support employees and reduce workplace stress.
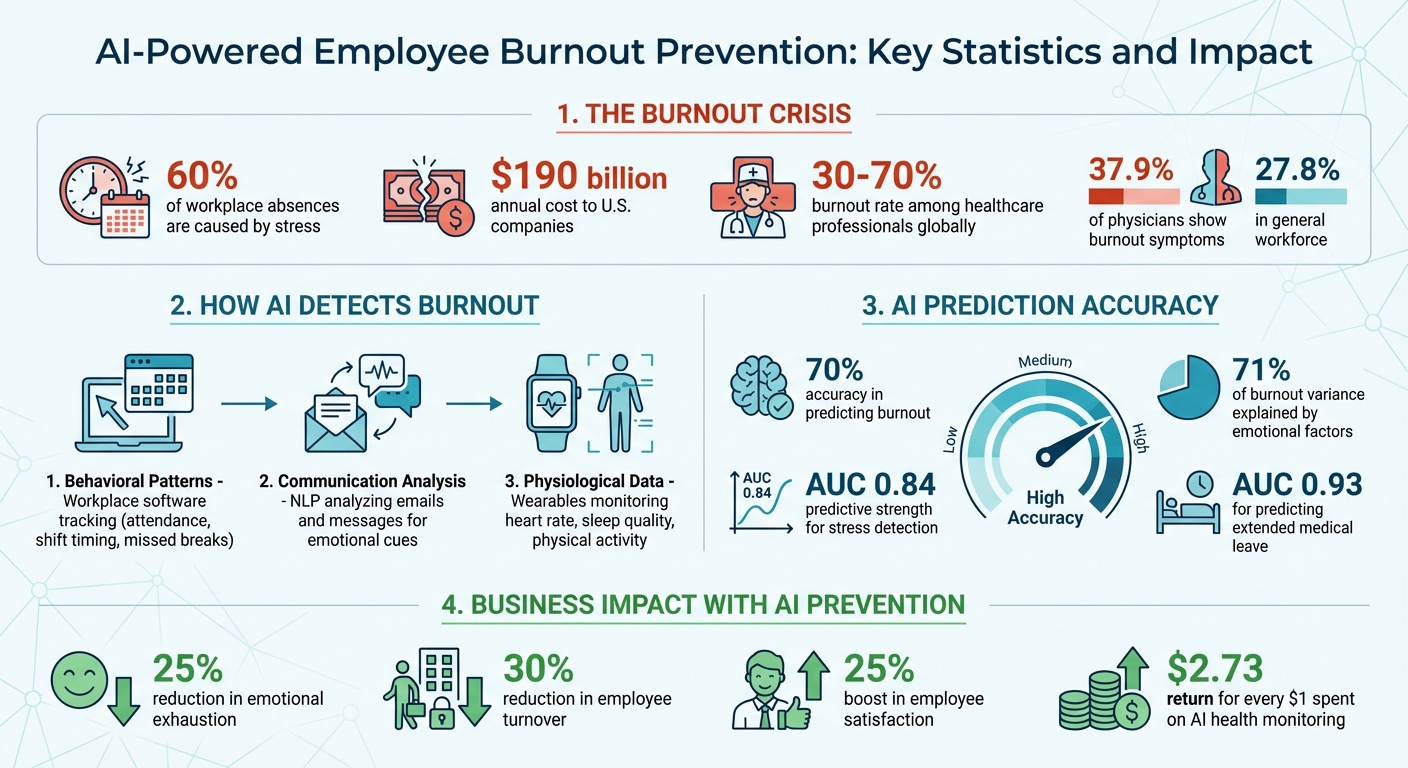
AI-Powered Employee Burnout Prevention: Key Statistics and Impact
What Employee Burnout Is and How It Affects Workplaces
What Burnout Means
Burnout is a psychological response to chronic, unmanaged stress in the workplace. The World Health Organization (WHO) has classified it as an occupational phenomenon in the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-11), though it’s not considered a medical condition [2][3].
Burnout typically shows up in three main ways: emotional exhaustion, which includes physical fatigue and mental weariness; depersonalization, marked by cynicism and a sense of detachment; and a diminished feeling of personal achievement [2][3][4][5]. Employees experiencing burnout might report constant tiredness, difficulty sleeping, or even frequent headaches [2][5].
The underlying causes of burnout are often a mix of immediate and structural workplace issues. Heavy workloads, understaffing, and long hours create immediate pressure, while factors like rigid hierarchies, unclear roles, limited autonomy, and conflicts between work and family life amplify the strain [2][3][4][5]. When workers are expected to meet high demands without having much control over how they manage their tasks, it creates a toxic imbalance that’s hard to sustain.
The effects of burnout extend far beyond individual employees, leading to broad organizational challenges that can be costly.
What Burnout Costs Businesses
Burnout doesn’t just affect individuals – it disrupts entire workplaces. It hampers decision-making, stifles creativity, and drags down productivity [2]. These measurable impacts make it critical for organizations to identify and address burnout before it spirals into larger problems.
The statistics are alarming. In healthcare alone, burnout rates among physicians and nurses hover between 30% and 70% globally [3]. A study comparing different professions found that 37.9% of physicians exhibited burnout symptoms, compared to 27.8% in the general workforce [4]. Between 2020 and 2021, physicians reported a 16.1% decline in their ability to balance work and personal life [4].
From an operational perspective, burnout drives up absenteeism, employee turnover, and reliance on temporary staff – all of which are expensive to manage [2][3]. It also creates administrative headaches, as organizations struggle to handle medical leave and maintain consistent service levels when seasoned employees leave. In high-stress fields like social work, the stakes are even higher: burnout has been linked to a 55.6% higher risk of suicide among social workers compared to the general working-age population [2].
| Burnout Dimension | What It Looks Like | Business Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Emotional Exhaustion | Fatigue, feeling overwhelmed, energy depletion | Higher absenteeism, reduced productivity [2] |
| Depersonalization | Cynicism, detachment from colleagues or clients | Lower service quality, strained relationships [2][4] |
| Reduced Accomplishment | Negative self-perception, dissatisfaction with work | Increased turnover, loss of skilled workers [2] |
ODSC Webinar | Predicting Employee Burnout at Scale
Data Sources AI Uses to Detect Burnout
AI identifies burnout by analyzing various data streams, combining behavioral patterns from workplace tools, sentiment analysis from communication, and physiological data from wearables. Each data source contributes distinct insights, helping AI create a well-rounded picture of employee well-being. Let’s dive into how these data streams work together.
Behavioral Patterns from Workplace Software
Workplace tools generate a steady flow of data that AI can analyze to flag signs of stress. Metrics like attendance, shift timings, and workload patterns help identify behaviors that might indicate burnout – such as consistently starting work too early or staying late [6][4].
For instance, a study by Shionogi & Co., Ltd. used an XGBoost machine learning model to analyze teleworking employees. It found that remote workers who frequently skipped lunch or worked irregular hours were at higher risk of stress. Meanwhile, for those working on-site, arriving too early or late was a more significant indicator. This model achieved an AUROC (Area Under the Receiver Operating Characteristic curve) score of 0.84, showcasing its predictive strength [6].
AI also tracks trends like missed breaks and recovery time between shifts. To refine predictions, modern systems group employees into "neighborhood clusters" based on shared work styles, rather than using one-size-fits-all models. This nuanced approach significantly improves accuracy [6].
Communication Sentiment Analysis
AI leverages Natural Language Processing (NLP) to assess emails, chat messages, and other written communications for emotional cues linked to burnout. It looks for signs of depersonalization – such as cynical or detached language – along with negative emotions, low mood, or feelings of inadequacy [4][2].
"The findings suggest a simple set of indicators can predict burnout and could be used for screening." – Güveyi et al. [4]
By analyzing linguistic patterns over time, AI can detect subtle shifts in emotional tone before burnout escalates. Research shows that 71% of burnout variance can be explained by key emotional and mental health factors like depression and connectedness [4]. AI organizes text into categories like "social safeness" (a sense of belonging) and "aliveness" (positive self-perception), offering a more objective and reliable analysis than traditional methods [4].
While communication analysis highlights emotional trends, integrating physiological data from wearables provides another layer of precision.
Physiological Data from Wearable Devices
Wearable devices offer continuous, objective data that complements subjective self-reports. AI evaluates metrics like heart rate variability, sleep quality (duration, efficiency, and timing), and physical activity (steps, distance, and calories burned) to uncover biological responses to stress [6][2].
The relevance of specific metrics often depends on work style. For remote employees, heart rate changes and activity levels are stronger indicators of stress. In contrast, for office-based workers, sleep patterns and calorie burn are more telling [6]. In the Shionogi study, Fitbit Charge 4 devices tracked daily metrics, and the AI model grouped employees based on teleworking rates. The system predicted stress levels for the upcoming week with an impressive AUC of 0.84. For remote workers, heart rate variability emerged as a key stress predictor, while for on-site employees, sleep duration and calorie burn were more critical [6].
When combined with work-style insights, wearable data enables AI models to achieve predictive accuracy levels (AUC of 0.84 to 0.85) far beyond traditional annual stress assessments [6]. This integration of behavioral, emotional, and physiological data ensures a deeper understanding of employee well-being.
AI Algorithms and Techniques for Burnout Prediction
AI is reshaping how workplace data is analyzed, turning raw information into meaningful insights for predicting burnout risks. By applying supervised learning, deep learning, and unsupervised clustering, these algorithms reveal intricate patterns within data, helping organizations anticipate and address burnout effectively [2]. Below, we explore some key AI methods driving these predictions.
Sentiment Analysis for Emotional Indicators
Sentiment analysis, powered by Natural Language Processing (NLP), examines workplace communication to detect emotional markers tied to burnout’s three core dimensions: emotional exhaustion (feeling overwhelmed), depersonalization (cynical attitudes), and reduced personal accomplishment [2]. For instance, phrases reflecting "negativism", "detachment", or "hopelessness" are red flags for chronic stress. Tools like Aidx.ai’s ATI monitor subtle emotional changes in real time [1], mapping shifts from initial enthusiasm during the "honeymoon phase" to later stages of "stagnation" or "apathy." These emotional shifts often signal the early stages of burnout [4].
Pattern Recognition and Predictive Modeling
By analyzing behavioral, emotional, and physiological data, pattern recognition algorithms categorize employees into different burnout risk groups. Unsupervised methods like k-means clustering group employees into high, intermediate, or low-risk categories without needing pre-labeled data [2]. Meanwhile, supervised learning models, trained on datasets such as Maslach Burnout Inventory scores, predict burnout risks either as binary outcomes or across multiple levels. Algorithms like Logistic Regression, Random Forest, Support Vector Machines (SVM), and XGBoost are frequently used to process complex workplace data [3].
Deep learning frameworks take this a step further. Architectures like FT-Transformers and TabNet, with multi-head attention, analyze interactions between demographic, clinical, and organizational features. These advanced techniques refine predictions, enabling more precise individual risk assessments.
Machine Learning Models for Risk Scoring
Machine learning models use prior analyses to deliver personalized burnout risk scores. Stacked ensemble models, which combine approaches like Transformers, XGBoost, and Logistic Regression, enhance predictive accuracy and reliability [3]. For example, a Romanian hospital study demonstrated the effectiveness of a stacked ensemble model paired with SHAP analysis, achieving a ROC AUC of 0.70 for burnout prediction and 0.93 for forecasting extended medical leave [3].
Explainable AI (XAI) methods, such as SHAP, help demystify these models by identifying key factors – like tenure, age, or specific clinical conditions – that impact an individual’s risk score. To address potential biases in the models, techniques like SMOTE for balancing datasets and regularization methods like LASSO or Elastic Nets are often applied [3].
sbb-itb-d5e73b4
How Aidx.ai Corporate Helps Prevent Burnout
Aidx.ai Corporate steps in to identify burnout risks long before employees even notice symptoms themselves [8]. Its Adaptive Therapeutic Intelligence (ATI) System™ keeps an eye on behavioral and emotional signals – like stress, indecisiveness, and feelings of impostor syndrome – in real time [1]. This forward-thinking approach tackles a pressing issue: nearly 60% of workplace absences stem from stress, costing U.S. companies between $125 billion and $190 billion annually in healthcare expenses [2][7].
By catching these early warning signs, Aidx.ai Corporate equips leaders with insights they can act on immediately.
Executive Dashboard and Team Analytics
Aidx.ai’s Executive Dashboard gives leaders a bird’s-eye view of team dynamics while safeguarding employee privacy. It aggregates and analyzes data at the team or department level, highlighting trends in stress, job satisfaction, and burnout risk – all without revealing individual conversations [7][8]. This allows leaders to pinpoint high-risk teams and make targeted adjustments, like redistributing workloads or enhancing wellness programs, without compromising anyone’s privacy [1].
The platform goes beyond just data collection. Its integrated planner tracks actionable metrics like goals, to-do lists, and progress indicators, turning insights into meaningful and lasting changes [1]. Importantly, the system operates passively in the background, analyzing existing workplace patterns without disrupting workflows [9][8]. As CEO Natalia Komis explains:
"Discover how we’re creating a preventative tool that supports people and organizations before crisis hits, not after" [1].
This approach is a stark departure from traditional burnout management methods.
Comparison: Traditional vs. Aidx.ai Approach
| Feature | Traditional Burnout Management | Aidx.ai Corporate Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Timing | Reactive – intervenes only when burnout is visible [2] | Proactive – detects risks weeks before employees notice symptoms [8][11] |
| Data Source | Annual surveys or clinical diagnoses [2][4] | Real-time ATI tracking and daily check-ins [1] |
| Methodology | Generic wellness advice or static chatbots | Adaptive Therapeutic Intelligence using CBT, DBT, and ACT techniques [1] |
| Accessibility | Limited to scheduled sessions with practitioners | 24/7 voice-first AI coaching, always available [1] |
| Privacy Measures | Often intrusive, focusing on individuals [9] | Aggregated insights focusing on team trends [10] |
| Outcomes | High administrative burden, lower productivity, higher turnover [9] | 30% reduction in turnover, 25% boost in employee satisfaction [7] |
Companies using AI-driven burnout prevention tools like Aidx.ai have seen emotional exhaustion among employees drop by 25%, with an average return of $2.73 for every dollar spent on health monitoring [7]. The platform’s voice-first interface also allows employees to share emotions more naturally, enabling the AI to detect stress patterns that text-only systems might miss [1].
How to Use AI for Burnout Prevention
Using AI to prevent burnout means weaving it seamlessly into your existing systems. Companies that succeed in this area focus on two main goals: creating a culture that values data-driven insights over gut feelings and introducing technology in a way that doesn’t disrupt daily workflows. This approach helps organizations stay ahead of burnout by relying on actionable data.
Building a Data-Driven Culture
Shifting from reactive wellness programs to proactive burnout prevention starts with trusting the data. Machine learning can predict burnout in 70% of cases by identifying early warning signs – patterns that traditional surveys often miss entirely [2]. Leaders need to see these AI insights as tools for improving workforce well-being, not as a means of micromanaging or surveillance.
When interpreting AI insights, organizations should focus on four psychological pillars: social safeness, internal aliveness, hope and meaning, and empathy and energy. These categories are strong indicators of burnout risk [4]. For instance, if your dashboard shows declining scores in these areas for a specific team, it’s a signal to reassess workloads, team dynamics, or available resources – not to tighten control.
Privacy is critical for building trust. Employees need to feel confident that their individual data and conversations are secure. Tools like Aidx.ai Corporate ensure privacy through aggregated data and secure systems, encouraging honest feedback and improving the accuracy of AI predictions.
Once trust is established, integrating AI tools into daily operations becomes the logical next step.
Adding AI Tools to Existing Workflows
The best AI tools fit smoothly into existing routines without creating unnecessary hurdles. Low-friction deployment is key – using cross-platform Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) eliminates the need for complex IT setups. Aidx.ai’s PWA model allows employees to access support on any device without dealing with downloads or complicated logins.
Voice-first integration is another game-changer. Unlike text-based systems that keep employees tied to their desks, voice-chat features let them engage with AI tools during commutes, walks, or other moments of downtime. This flexibility increases participation because it works with their existing habits instead of requiring new ones.
AI tools should also connect insights to actionable workflows. For example, when AI flags an issue like poor work-life balance, it shouldn’t just alert the employee – it should help them set goals, schedule breaks, and track progress. This closed-loop approach ensures that insights lead to real, measurable outcomes.
To get the most out of AI, integrate data from multiple sources like wearables, digital sensors, and self-assessment surveys. AI’s ability to spot patterns across complex datasets is unmatched. For example, a combination of reduced step counts, shorter sleep durations, and increased after-hours emails might indicate burnout – something no single metric could reveal on its own.
Finally, provide real-time dashboards for occupational health teams. In one study involving 1,244 healthcare professionals, an AI framework achieved a ROC AUC of 0.93 in predicting extended leaves [3]. These dashboards give teams immediate visibility into stress indicators, allowing for quicker and more effective interventions.
Future Trends in AI Employee Stress Assessment
The future of AI-driven stress assessment is shaping up to be more precise and actionable. Emerging tools are moving beyond static surveys, leveraging Explainable AI (XAI) techniques like SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations) to pinpoint the exact factors driving burnout risks. This added layer of clarity not only builds trust but also enables more targeted and effective interventions[3].
Multitask learning is also making waves by analyzing multiple interconnected factors – such as mood, stress levels, and physical health – rather than focusing on a single outcome. Paired with data from wearable devices, these systems provide a richer, more holistic view of an employee’s well-being compared to traditional self-reported questionnaires[2].
Another exciting development is the rise of integrated health frameworks that replace isolated systems. For example, in September 2025, a team led by Maria Valentina Popa implemented an AI-based framework in a Romanian hospital, involving 1,244 healthcare professionals. By combining XGBoost and FT-Transformer models, the system effectively predicted burnout, Long COVID, and extended sick leave. It achieved a remarkable ROC AUC of 0.93 for predicting extended medical leave, showcasing its real-world potential[3].
Advanced deep learning models like TabNet are also stepping into the spotlight. These frameworks excel at processing high-dimensional datasets, merging demographic, clinical, and organizational information. Unlike older methods, they can uncover complex, non-linear patterns that were previously undetectable[3].
Finally, Adaptive Therapeutic Intelligence (ATI) is shifting the focus from generic wellness programs to personalized coaching systems that adapt to individual needs over time. With voice-first interfaces, employees can access support during daily routines, such as commutes or breaks. This proactive approach aims to address stress before it escalates into a crisis, marking a significant shift in how organizations tackle employee well-being[1].
These advancements signal a future where AI not only identifies stress but also provides tailored, preventive solutions to support employees in real time.
Conclusion
AI is reshaping how organizations tackle burnout by identifying early warning signs through real-time data analysis. Unlike traditional methods that often overlook the gradual buildup of exhaustion, modern AI systems dive into behavioral patterns, communication tones, and physiological data to predict burnout with greater accuracy [2]. Considering that around 60% of work absences are linked to workplace stress [2], the need for early intervention has never been more apparent. This technology offers immediate insights, moving far beyond outdated annual assessments.
What sets AI apart is its ability to handle complex, non-linear data. Traditional statistical models often falter when faced with such intricacies. In contrast, advanced AI systems pull data from workplace tools and wearables, providing a comprehensive view of employee well-being [3]. Tools like SHAP (a type of Explainable AI) go a step further by breaking down model decisions, helping managers pinpoint specific factors – such as tenure, age, or underlying health conditions – that contribute to an employee’s risk of burnout [3].
These capabilities empower managers to make more informed decisions. For companies ready to take the leap, platforms like Aidx.ai Corporate offer practical solutions. Built on Adaptive Therapeutic Intelligence (ATI), this platform combines real-time team analytics with 24/7 voice-enabled coaching. Instead of waiting for scheduled sessions, employees can address stress as it arises, seamlessly integrating support into their daily routines. As Natalia Komis, CEO of Aidx.ai, puts it:
"We’re creating a preventative tool that supports people and organizations before crisis hits, not after" [1].
With structured dashboards that balance actionable insights and privacy, leaders can reduce sick days and boost employee retention.
The future of workplace well-being lies in personalized, data-driven interventions that evolve with individual needs. By incorporating AI into daily operations, organizations can address the root causes of stress and burnout, fostering healthier and more productive teams.
FAQs
How does AI predict employee burnout?
AI systems can now estimate the risk of employee burnout by examining a mix of data sources, including HR records, self-reported surveys, and optional inputs like wearable devices or workplace collaboration tools. By analyzing this information, these systems detect patterns – such as excessive overtime, signs of emotional exhaustion, or unusual work habits – that may indicate burnout.
Machine learning models then use these patterns to categorize employees into different burnout risk levels: low, moderate, or high. Some advanced platforms, like Aidx.ai’s Adaptive Therapeutic Intelligence (ATI), take it a step further by continuously updating their predictions and offering tailored coaching solutions. This proactive approach helps organizations address burnout risks before they become more serious.
How can AI help prevent employee burnout in the workplace?
AI plays a key role in tackling employee burnout by spotting early warning signs through constant analysis of factors like work hours, communication habits, and stress indicators. With machine learning, it becomes possible to identify emotional exhaustion before it spirals, allowing companies to step in early. This proactive approach can lead to fewer sick days, better employee retention, and improved overall well-being.
Beyond just identifying issues, AI offers personalized support that adapts to an employee’s unique stress patterns. Tools like cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and mindfulness exercises can be accessed anytime through chat or voice interfaces, giving employees immediate ways to manage stress. Meanwhile, managers gain access to anonymized insights via dashboards, helping them make data-driven decisions while respecting individual privacy.
How does AI protect employee privacy while assessing burnout risk?
AI prioritizes employee privacy through advanced measures like encryption, anonymization, and user-controlled settings. For instance, personal data – such as stress levels or emotional patterns – is encrypted and stripped of any identifying details before analysis. This ensures that no individual can be directly associated with the data, keeping raw information secure and confidential.
Platforms like Aidx.ai take this a step further by offering features such as incognito mode and consent-based settings. These tools empower employees to pause data collection or choose what information is tracked. Additionally, corporate dashboards only present aggregated insights, avoiding exposure of individual conversations or detailed metrics. These privacy safeguards allow AI to assess burnout risks effectively while respecting the confidentiality employees expect.



