Real-time emotion tracking helps identify stress as it happens, allowing for immediate action to prevent burnout. By analyzing physiological signals (like heart rate variability) and behavioral cues (like voice tone), tools such as wearables and apps provide insights into stress patterns throughout the day. This technology benefits both individuals and organizations by enabling timely interventions, such as relaxation techniques or workload adjustments, to improve well-being and productivity.
Key points:
- For individuals: Tools detect stress spikes and suggest immediate solutions like breathing exercises or breaks.
- For organizations: Aggregated, anonymized data reveals team stress trends, guiding decisions to adjust workflows or offer support.
- Privacy matters: Clear consent, data encryption, and anonymity ensure ethical use.
Real-time emotion tracking shifts stress management from reactive to preventive care, benefiting health and workplace efficiency.
What Real-Time Emotion Tracking Is and Why It Matters
What Is Real-Time Emotion Tracking?
Real-time emotion tracking is a system that continuously monitors your emotional and stress levels by analyzing multiple data sources. It gathers physiological signals like heart rate variability, skin conductance, and skin temperature, along with behavioral cues such as voice tone, facial expressions, and even typing speed. To complement this, users may provide occasional self-assessments through smartphone check-ins. Machine learning algorithms then process all this information to classify your emotional state – whether you’re stressed, calm, or frustrated – and provide feedback in near real-time.
This kind of tracking focuses on short-term emotional shifts that occur throughout the day. By identifying stress early, it allows for timely intervention before it escalates. For instance, continuous monitoring might uncover recurring stress patterns linked to specific times or activities – details that traditional surveys could easily miss. By seamlessly integrating data from various sources, these systems deliver insights that are both timely and actionable.
How Real-Time Emotion Tracking Helps Manage Stress
One of the biggest advantages of real-time emotion tracking is its ability to detect stress early. It can pinpoint spikes in stress that you might not even be aware of, often tied to specific tasks or times of day. For example, a wearable device might notice a drop in heart rate variability and a rise in skin conductance during late-night work, signaling that it’s time to make adjustments.
When stress markers cross predefined thresholds, the system can prompt you to take a break or try relaxation techniques, offering a data-driven approach to managing stress. Over time, this feedback can help you identify which strategies work best for you.
On a larger scale, organizations can use anonymized, aggregated data to uncover broader stress patterns. For example, they might notice increased stress levels during certain project phases. With this information, leaders can make informed decisions about adjusting workloads, setting more realistic deadlines, or reallocating resources – all aimed at improving overall well-being in the workplace.
Real Time Stress Detection & Alleviation Application with Wearable Tech & Multi Language Support
How Real-Time Emotion Tracking Systems Work
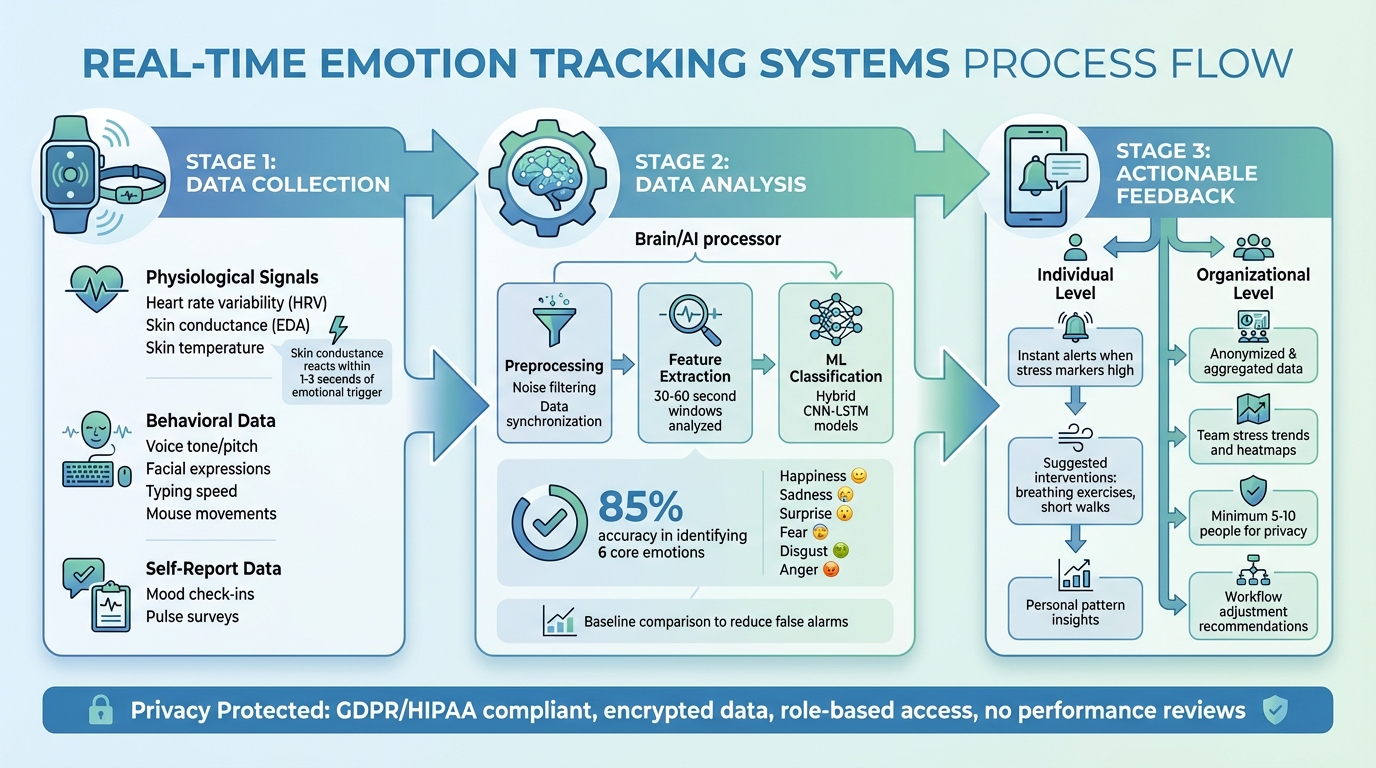
How Real-Time Emotion Tracking Systems Work: From Data Collection to Actionable Insights
Types of Data Used in Emotion Tracking
Real-time emotion tracking relies on three main types of data. Physiological signals are captured through wearable devices like smartwatches, which monitor heart rate and heart rate variability (HRV) using optical sensors. Wristbands or rings can measure skin conductance (also known as EDA) by detecting sweat gland activity through electrodes – this data often reacts within 1–3 seconds of an emotional trigger.[2][7]
Behavioral data provides another critical layer. Desktop or mobile apps analyze voice tone and pitch during conversations, while optional camera access can track facial expressions and subtle micro-movements that hint at mood changes. Even typing speed and mouse movement patterns can act as indirect indicators of stress.[3][6] Lastly, self-report data adds a personal touch. These are quick mood check-ins or pulse surveys where users log their feelings. This subjective input helps validate sensor data and fills in gaps that algorithms might overlook.[4]
By integrating these diverse data streams, the system creates a comprehensive emotional profile.
How Data Gets Analyzed and Turned into Feedback
Once collected, raw data undergoes a preprocessing stage. Noise filters remove motion artifacts, and data streams are synchronized. The system then divides the information into short windows – typically 30 to 60 seconds – and extracts key features like HRV, skin conductance patterns, voice prosody, and facial action units.[2][5]
Hybrid machine learning models, such as CNN-LSTM, classify these features into emotional states like "stressed", "calm", or "engaged." These models achieve about 85% accuracy in identifying six core emotions – happiness, sadness, surprise, fear, disgust, and anger – using data from EEG and facial analysis.[2] To reduce false alarms, the system compares new data against personal baselines and flags only significant deviations. For instance, if stress markers remain high for several minutes, the app might suggest a two-minute breathing exercise or recommend taking a short walk.[4][5]
For organizational use, individual data is anonymized and aggregated into team-level insights. Managers can view metrics like average stress levels, high-stress periods, or time-based heatmaps. However, these reports are only generated for groups of at least five to ten people to ensure individual privacy. This helps leaders identify trends – like increased stress during product launches – without exposing personal details.[4]
The result is actionable emotional feedback, backed by robust privacy measures.
Privacy and Ethics in Emotion Tracking
Privacy starts with clear and informed consent. Users must know what data is being collected, why it’s needed, how long it’s stored, and who can access it. They should also have the option to opt out or withdraw their consent at any time without facing any consequences. Systems adhering to GDPR and HIPAA guidelines ensure data collection is limited to what’s necessary, with all data encrypted during transmission and storage. Access is strictly limited to authorized personnel.[4]
Emotion data is strictly for wellbeing purposes – it is not to be used for performance reviews, disciplinary actions, or any form of discrimination. Platforms often include features like incognito modes for private emotional exploration and enforce clear policies prohibiting misuse. Role-based permissions and de-identification processes ensure managers cannot identify individuals, keeping analytics aligned with ethical and legal standards.[4]
sbb-itb-d5e73b4
How to Set Up Real-Time Emotion Tracking at Work
Finding Where Stress Levels Are Highest
The first step in managing workplace stress is identifying where it’s most concentrated. Start by analyzing existing data such as absenteeism records, turnover rates, and productivity metrics. For example, teams with noticeable spikes in sick days during end-of-quarter crunch times or roles that often require overtime may indicate higher stress levels. HR incident reports and self-reported surveys can also reveal patterns, like increased stress on Monday mornings or burnout after lengthy meetings.
To dig deeper, consider using anonymous pulse surveys or reviewing existing biometric data. This approach helps you identify trends while minimizing privacy concerns. For instance, if your sales team consistently reports elevated stress during product launches, you can aim to reduce their stress levels during these periods by 20% through targeted tracking efforts [3][8]. Always ensure participation is voluntary to build trust and encourage honest feedback. These insights will help you choose the most effective tracking tools.
Selecting Emotion Tracking Tools and Platforms
When selecting emotion tracking tools, aim for a balance between accuracy and ease of use. Wearables or apps that monitor stress indicators in real time – like skin conductance sensors – are highly effective, as they can react within 1–3 seconds of an emotional trigger [7]. Features such as wireless data transfer and long battery life make these tools more practical for daily use, reducing the hassle for employees.
Platforms like Aidx.ai offer a comprehensive solution by combining real-time stress tracking with AI-driven coaching. Their platform includes voice-enabled therapeutic conversations based on proven techniques like CBT, DBT, ACT, and NLP, along with team dashboards that display aggregated well-being metrics. This allows managers to monitor trends – such as average stress levels or high-stress periods – without accessing individual employee data. To ensure a smooth rollout, start with a pilot program involving one volunteer team for 1–2 weeks. This trial period will help you test integration, gather feedback, and refine the process before expanding company-wide.
Creating Response Plans Based on Tracking Data
Once you’ve gathered data, the next step is turning insights into actionable strategies. Set up alerts to prompt immediate interventions, such as encouraging employees to take a short walk or practice breathing exercises when stress markers remain high. Weekly analytics can also help you identify patterns, like stress spikes after meetings, allowing you to implement solutions such as five-minute check-ins or rebalancing workloads for overburdened teams.
For more sustained stress, deploy support measures like coaching or therapy. Train managers to handle these situations with care and sensitivity. For example, Aidx.ai’s Corporate solution offers voice-based CBT sessions that employees can access as soon as stress alerts are triggered. This transforms insights into real-time support. Track the effectiveness of your response plans by monitoring metrics like reduced sick days, improved morale, and lower turnover. Use these results to refine your approach and create a healthier, more productive work environment.
Daily Practices for Stress Reduction Using Tracking Data
Personal Stress Management Techniques
Respond to stress alerts from your wearable as soon as they arise. For instance, if your device detects heightened stress through heart rate variability changes, try the 4-7-8 breathing method: inhale for 4 seconds, hold for 7 seconds, and exhale for 8 seconds. This simple technique can help you quickly regain control. Similarly, if you notice facial tension alerts, take a brief moment – just 1-2 minutes – to tune into your body’s sensations and relax.
When negative thoughts pop up, like "I’ll never finish this project", reframe them into something more constructive, such as "This deadline is tough, but I can handle it." Tools like Aidx.ai’s voice-enabled sessions can guide you through this process, helping to shift your mindset in real time.
Tracking your emotions over a week or two can reveal patterns, like when your stress levels tend to peak. Use this insight to schedule short, 5-minute breaks before those high-stress moments. By relying on personal baseline data, you can time these interventions effectively. Reviewing weekly logs allows you to fine-tune your habits, making adjustments as needed. Wearable devices powered by hybrid CNN-LSTM models can classify emotions like anger or anxiety with up to 85% accuracy, giving you reliable data to guide your stress management efforts [2].
These individual techniques work hand-in-hand with broader workplace strategies, ensuring stress is addressed both at a personal level and within organizational systems.
Using Data to Improve Workplace Conditions
The insights you gather personally can also inform workplace improvements. For example, organizations can use aggregated emotion data to create a healthier work environment while maintaining employee privacy. If team data shows that stress levels consistently spike between 2-5 PM during meetings, managers can make changes – shortening meeting durations, adding breaks, or redistributing tasks during those hours.
Anonymized metrics can also guide workload adjustments. For instance, if skin conductance data reveals a 30% stress increase during deadline periods, managers might reassign tasks or bring in temporary support to ease the pressure. Similarly, if data highlights tension after specific interactions, shifting from email to voice calls for sensitive discussions could help improve team dynamics and reduce stress [2].
This approach uses real-time insights to create proactive, data-driven solutions for managing stress, both individually and within teams. It ties into the broader strategy of addressing stress as it happens, ensuring a balanced and supportive environment for everyone.
Conclusion
Real-time emotion tracking is changing how we approach stress management, shifting from reactive solutions to proactive care. By monitoring factors like heart rate variability, skin conductance, and voice tone, these systems can identify stress within 1 to 3 seconds – long before it escalates into burnout [7]. When stress levels rise, wearables deliver instant suggestions for relief, helping to interrupt the cycle before it takes hold.
This approach benefits both individuals and organizations. The detect–prompt–respond process not only addresses stress in the moment but also builds resilience over time. Weeks of tracking can reveal personal patterns, such as which tasks or times of day are most draining, and which coping strategies are most effective. On a larger scale, organizations can use aggregated data to redesign workflows and reduce burnout risks [7].
Platforms like Aidx.ai are bringing this vision to life for individuals and teams alike. For employees, Aidx offers passive emotion tracking combined with voice-enabled AI coaching. Using techniques grounded in CBT, DBT, ACT, and NLP, it delivers personalized interventions right when stress spikes. The platform’s Adaptive Therapeutic Intelligence learns your unique patterns over time, making its support more tailored and effective.
Natalia Komis, CEO of Aidx.ai, explains: "Discover how we’re creating a preventative tool that supports people and organizations before crisis hits, not after." [1]
For organizations, Aidx provides team dashboards that display anonymized wellbeing metrics, including stress trends, job satisfaction, and burnout risks. This allows leaders to make informed decisions based on data rather than assumptions – all while preserving employee confidentiality. The outcome? Fewer sick days, reduced turnover, and a workplace culture where stress is addressed early, not ignored until it causes harm.
Real-time emotion tracking is already proving its effectiveness. Whether you’re an individual aiming to understand your stress patterns or a company striving to create a healthier work environment, these tools enable early intervention and precise solutions. Start small and pair technology with human support to make meaningful progress.
FAQs
How can real-time emotion tracking help prevent burnout?
Real-time emotion tracking offers a way to tackle burnout by spotting stress early and offering practical solutions. Using tools like biometric sensors, voice analysis, and AI, it monitors emotional patterns and flags rising stress levels.
When these warning signs are caught early, individuals can take steps like incorporating mindfulness techniques or rebalancing their workloads. For organizations, the aggregated data provides a clearer picture, enabling smarter resource management, stronger team collaboration, and proactive measures to lower burnout risks.
What kind of data is used in real-time emotion tracking?
Real-time emotion tracking works by gathering and analyzing several types of data to gauge emotional states. This includes biometric data such as heart rate variability and skin conductance, as well as facial expressions and voice patterns that help infer emotions. Additionally, users often contribute through self-reported emotions, offering personal insights. Some advanced systems go a step further by examining behavioral data, which can reveal stress patterns and emotional trends over time. By integrating these diverse inputs, these tools aim to provide a well-rounded view of emotional well-being while prioritizing privacy for users.
How do emotion tracking systems protect user privacy?
Emotion tracking systems take user privacy seriously by implementing data encryption to safeguard information and adhering to GDPR and other privacy guidelines. These systems focus on analyzing anonymized and aggregated data, steering clear of individual tracking unless users provide explicit consent. This approach keeps emotional data secure and confidential.



